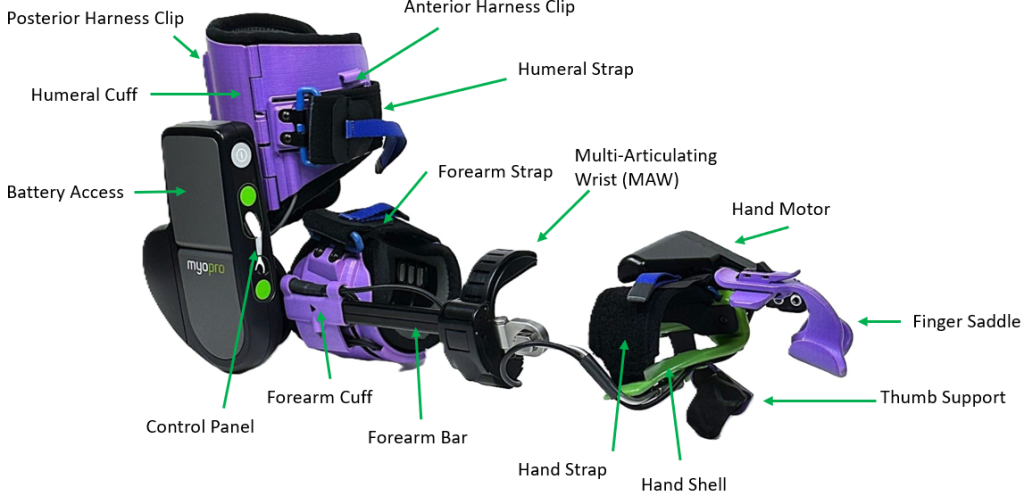

Originally developed at MIT with Harvard Medical School, the MyoPro arm and hand orthosis device works by reading the faint nerve signals (myoelectric signals) from the surface of the skin (fully non-invasive, with no implants) then activating small motors to move the limb as the user intends (no electrical stimulation).
The user is completely controlling their own hand, wrist, elbow, and arm, while the myoelectric arm brace amplifies weak muscle signals to help move the upper limb. It has been called “power steering for your arm.”
While there are many brace products for those who have lost their arms, hands or legs, and while there are orthotic products to support weak legs, MyoPro is the only wearable myoelectric device on the market to help restore function for those who still have their arms and hands but are unable to use them.


The first myoelectric prosthesis was created between 1944-1948 by Reinhold Reiter, a physics student at Munich University. Reiter recognized that to work properly, the device needed to obtain maximum information from the myoelectric signal. Over the past 50 years, the technology has moved from single muscle control of a single prosthesis function to more complex muscle group activity control of multifunction prostheses. Central to these changes have been developments in extracting information from the myoelectric signal.
Later work expanded the concept of myoelectric control to orthoses for upper extremity impairment. By supporting research in 1990, the VA promoted and inspired the development for a future myoelectric orthosis that could benefit Veterans who have upper extremity impairment. In 2006, work in myoelectric upper extremity orthoses at MIT was commercialized resulting in the development of the MyoPro myoelectric elbow-wrist-hand orthosis (EWHO).

| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |